VPC Components
VPC Networking Components
You can use the following components to configure networking in your VPC:


Networking Components

A VPC is a virtual network specific to you within AWS for you to hold all your AWS services. It is a logical data center in AWS and will have gateways, route tables, network access control lists (ACL), subnets and security groups.
Things to note:
Each subnet exists within 1 availability zone.
Security groups are stateful, ACL’s are stateless
VPC’s can be peered within the same account and across AWS accounts
Transitive peering is not allowed, meaning you cant hop from one VPC to another, via another VPC. You must have direct access.
Why use a VPC?
When you open up a service within a public cloud, it is effectively open to the world and can be at risk to attacks from the internet. In order to lock your instances down and secure them against attacks from the outside, you lock them within a VPC. The VPC restricts what sort of traffic, IP addresses and also the users that can access your instances.
This prevents unwanted guests accessing your resources and secures you from things like DDOS attacks. Not all services require access to the internet, so those can be locked away safely within a private network. You can then expose only certain machines to the internet.
Obviously, if you wanted to install software or access the internet from private instances that are blocked off from the internet, then this is a problem. However, there are a few solutions to this problem that I will cover next.
NAT Instances
A NAT instance can be used to solve the problem “how do I install things from the internet on my secured private instances”?
A NAT instance is created in a public subnet with access to the internet. Once you allow access from your private instance to your NAT, your private instance will then be able to make requests to the internet. This access is one way i.e. someone from the internet cannot access your instance.
Things to note:
A NAT instance must be in a public subnet
It must have an Elastic IP
There must be a route from your private subnet into the NAT instance
You can manually create high availability using Autoscaling groups and multiple subnets
Different to a Bastian because a NAT is used to provide internet access to private instances, a Bastian is used to administer instance using SSH for example.
They are now sort of deprecated and replaced with NAT Gateways
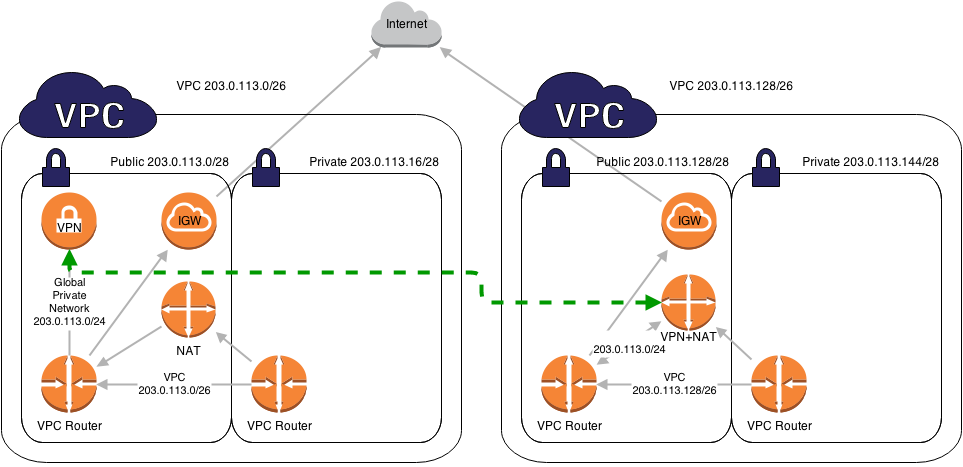
Image taken from wrathofchris.wordpress.com
NAT Gateways
NAT Gateways have basically replaced NAT instances as they allow the same access to the internet from a private subnet with the same security. However, they are much easier to set up and scale, as this is all managed by Amazon.
Things to note:
Scale automatically up to 10Gbps
No need to manually patch — amazon takes care of this
Not associate with security groups
automatically assigned a public IP
Network Access Control Lists (ACL)
By default, a VPC will come with a Network ACL and it will allow all inbound and outbound traffic. However, if you create a default Network ACL, it will block all inbound and outbound traffic, and you will have to manually allow traffic yourself.
Each subnet within a VPC must be connected to a Network ACL, however, each subnet can only be connected to 1 VPC at a time. The ACL, however, can be connected to multiple different subnets.
Things to remember:
The Network ACL contains an ordered list of rules to allow traffic
The convention is to start from 100 rules and go up in increments of 100.
The rules will be considered in order to make sure if you want to allow all ssh access apart from a certain IP address, that you add your block rule before your allow all rule.
There are separate rules for inbound and outbound traffic, so you must set up rules for each.
They are stateless meaning responses to inbound traffic are dependent on outbound traffic rules and this applies the other way around.
Block IP address using Network ACL’s and not Security groups
Last updated