AWS Lambda Serverless
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Lambda executes your code only when needed and scales automatically, from a few requests per day to thousands per second. All you need to do is supply your code in one of the languages that AWS Lambda supports (currently Node.js, Java, C#, Go and Python).
Serverless architectures refer to applications that significantly depend on third-party services (knows as Backend as a Service or “BaaS”) or on custom code that’s run in ephemeral containers (Function as a Service or “FaaS”), the best-known vendor host of which currently is AWS Lambda

Another advantage of going serverless is that you no longer need to keep a server running all the time. The “server” suddenly appears when you need it, then disappears when you’re done with it. Now you can think in terms of functions instead of servers, and all your business logic can now live within these functions.
In the case of AWS Lambda Functions, this is called a trigger. Lambda Functions can be triggered in different ways: an HTTP request, a new document upload to S3, a scheduled Job, an AWS Kinesis data stream, or a notification from AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS).
In this blog, I’ll show you how to set up your own Lambda Function and, as a bonus, show you how to set up a REST API all in the AWS Cloud, while writing minimal code.
First, you’ll need an AWS account. If you don’t have one yet, start by opening a free AWS account here. AWS has a free tier that’s more than enough for what you will need for this tutorial.
Get AWS account by signup here
We’ll be writing the function isPalindrome, which checks whether a passed string is a palindrome or not. Lets walk through Complete Demo of How to write this function using Lambda
Above is an example implementation in JavaScript. Here is the link for gist on Github.
A palindrome is a word, phrase, or sequence that reads the same backward as forward, for the sake of simplicity we will limit the function to words only.
As we can see in the snippet above, we take the string, split it, reverse it and then join it. if the string and its reverse are equal the string is a Palindrome otherwise the string is not a Palindrome.
Creating the isPalindrome Lambda Function
In this step we will be heading to the AWS Console to create the Lambda Function:
Once you have AWS account Login to that account
Navigate to AWS services and search Lambda
Lambda is event driven function code can be written in different languages like node JS, Python

In the AWS Console go to Lambda.

And then press “Get Started Now.”

Lets write our function in Node JS, For runtime select Node.js 6.10 and then press “Blank Function.”

Skip this step and press “Next.”

For Name type in isPalindrome, for description type in a description of your new Lambda Function, or leave it blank. As we have selected node JS we need to add code for it, its simple function which takes 3 arguments event,Context, and callback
As you can see in the gist above a Lambda function is just a function we are exporting as a module, in this case, named handler. The function takes three parameters: event, context and a callback function.
The callback will run when the Lambda function is done and will return a response or an error message.For the Blank Lambda blueprint response is hard-coded as the string ‘Hello from Lambda’. For this tutorial since there will be no error handling, you will just use Null. We will look closely at the event parameter in the next few slides.

Scroll down. For Role choose “Create new Role from template”, and for Role name use isPalindromeRole or any name, you like.
For Policy templates, choose “Simple Microservice” permissions.

For Memory, 128 megabytes is more than enough for our simple function.
As for the 3 second timeout, this means that — should the function not return within 3 seconds — AWS will shut it down and return an error.Three seconds is also more than enough.
Leave the rest of the advanced settings unchanged.

Press “Create function.”

Congratulations — you’ve created your first Lambda Function. To test it press “Test.”

As you can see, your Lambda Function returns the hard-coded response of “Hello from Lambda.”
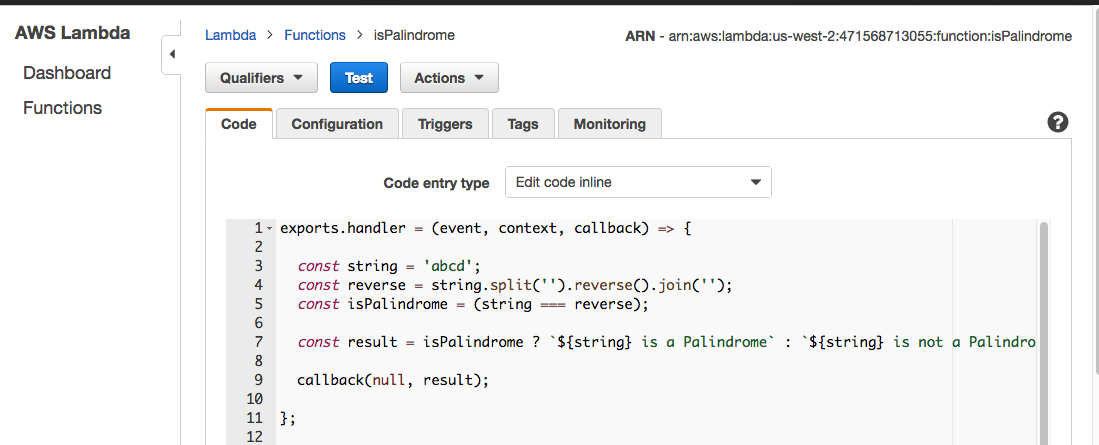
Now add the code from isPalindrome.js to your Lambda Function, but instead of return result use callback(null, result). Then add a hard-coded string value of abcd on line 3 and press “Test.”

The Lambda Function should return “abcd is not a Palindrome.”

For the hard-coded string value of “racecar”, The Lambda Function returns “racecar is a Palindrome.”
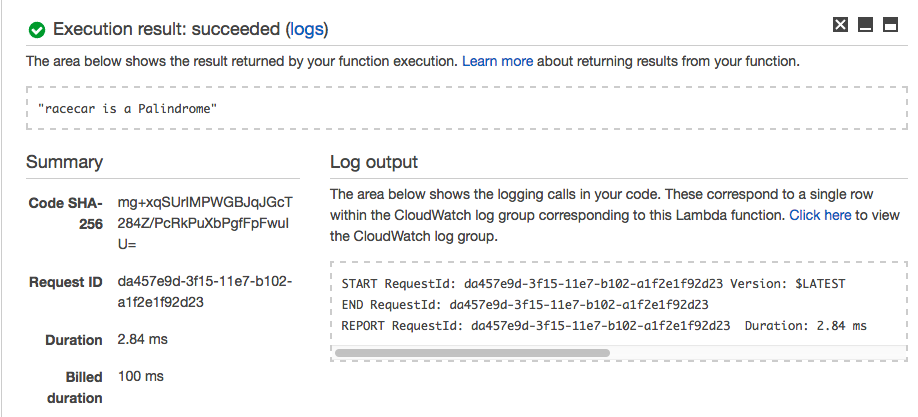
So far, the Lambda Function we created is behaving as expected.
In the next steps, I’ll show you how to trigger it and pass it a string argument using an HTTP request.
If you’ve built REST APIs from scratch before using a tool like Express.js, the snippet above should make sense to you. You first create a server, and then define all your routes one-by-one. Express can be used to create simple Http server and simple Node js api routes.
In this section, I’ll show you how to do the same thing using the AWS API Gateway. Where we will define API endpoints where we will hit code.
Go to AWS services and search API Gateway
Get started with API Gateway
Creating the API Gateway

Go to your AWS Console and press “API Gateway.”

And then press “Get Started.”

In Create new API dashboard select “New API.”

For API name, use “palindromeAPI.” For description, type in a description of your new API or just leave it blank.
Our API will be a simple one, and will only have one GET method that will be used to communicate with the Lambda Function.
In the Actions menu, select “Create Method.” A small sub-menu will appear. Go ahead and select GET, and click on the checkmark to the right.

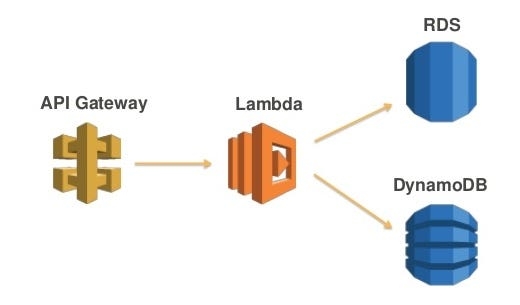
For Integration type, select Lambda Function.Here we are Connecting our API Gateway with Lambda function which we have written, Our lambda code can have code of getting data from RDS or any DB system like example below

Then press “OK.”

In the GET — Method Execution screen press “Integration Request.”

For Integration type, make sure Lambda Function is selected.

For request body passthrough, select “When there are no templates defined” and then for Content-Type enter “application/json”.

In the blank space add the JSON object shown below. This JSON object defines the parameter “string” that will allow us to pass through string values to the Lambda Function using an HTTP GET request. This is similar to using req.params in Express.js.
In the next steps, we’ll look at how to pass the string value to the Lambda Function, and how to access the passed value from within the function.

The API is now ready to be deployed. In the Actions menu click “Deploy API.”

For Deployment Stage select “[New Stage]”.
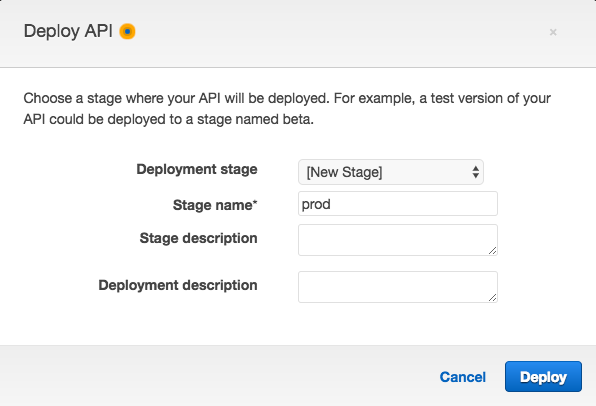
And for Stage name use “prod” (which is short for “production”).
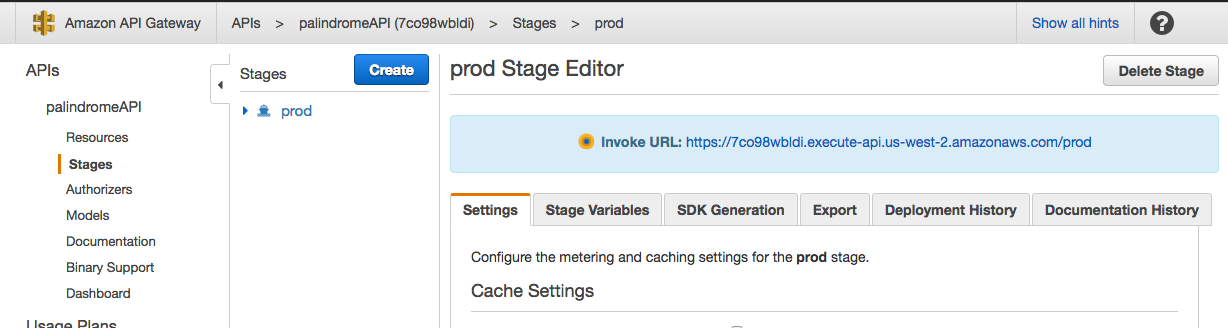
The API is now deployed, and the invoke URL will be used to communicate via HTTP request with Lambda. If you recall, in addition to a callback, Lambda takes two parameters: event and context.
To send a string value to Lambda you take your function’s invoke URL and add to it ?string=someValue and then the passed value can be accessed from within the function using event.string.
Modify code by removing the hard-coded string value and replacing it with event.string as shown below.

Now in the browser take your function’s invoke URL and add ?string=abcdto test your function via the browser.
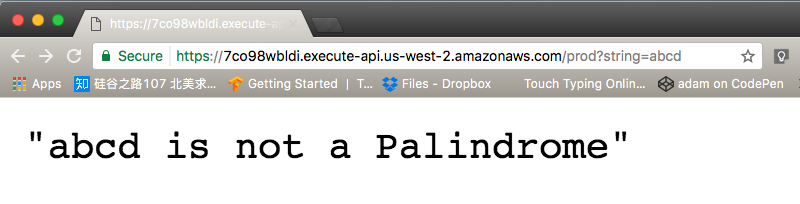
As you can see Lambda replies that abcd is not a Palindrome. Now do the same for racecar.
If you prefer you can use Postman as well to test your new isPalindrome Lambda Function. Postman is a great tool for testing your API endpoints, you can learn more about it here.
To verify it works, here’s a Palindrome:

And here’s a non-palindrome:

Congratulations — you have just set up and deployed your own Lambda Function! From Here you can explore more on writing lambda function which has complex Data fetch mechanism or Data store mechanism.
happy coding !!
Last updated