Microservices Architecture
What is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices is an architectural style in which large complex application is composed of two or more smaller services.
Wikipedia explains as :
The philosophy of the microservices architecture essentially equals to the Unix philosophy of “Do one thing and do it well”. It is described as follows: — The services are small — fine-grained to perform a single function. — The organization culture should embrace automation of testing and deployment. This eases the burden on management and operations and allows for different development teams to work on independently deployable units of code. — The culture and design principles should embrace failure and faults, similar to anti-fragile systems. — Each service is elastic, resilient, composable, minimal, and complete.
Monolithic Architecture V/S Microservices Architecture:
Microservices infographic
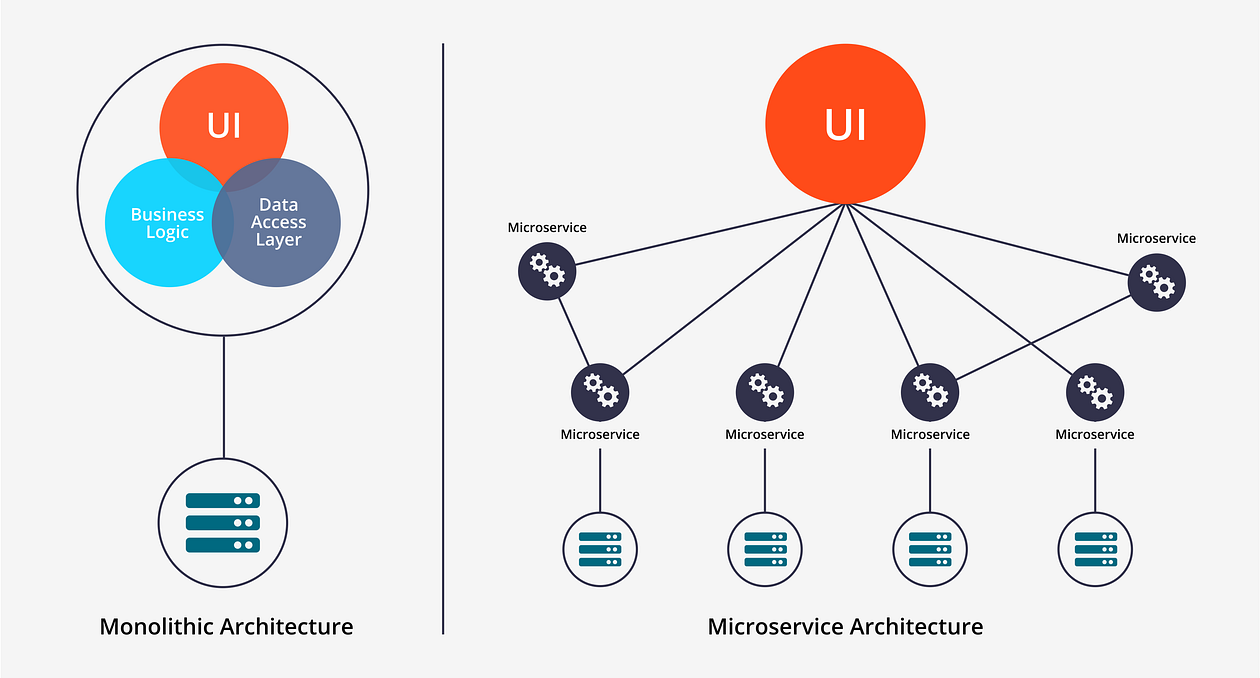
Advantages of Microservices Architecture are as below,
Microservices architecture gives developers the freedom to independently develop and deploy services. (No more Release Monday or Wednesday)
The code is organized around business capabilities.
Better fault isolation (No need to go through entire application logs to find fault cause)
Easy integration and automatic deployment; using open-source continuous integration tools such as Jenkins and The microservice architecture enables continuous delivery. (DevOps)
Easy to understand since they represent a small piece of functionality, and easy to modify for developers, thus they can help a new team member become productive quickly.
Work very well with containers, such as Docker.
Microservices simplify security monitoring because the various parts of an app are isolated. A security problem could happen in one section without affecting other areas of the project.
Successful Case Studies and Examples of Microservices Architecture Implementation — Netflix, eBay, Amazon, the UK Government Digital Service, Twitter, PayPal, The Guardian, and many other large-scale websites and applications have all evolved from monolithic to microservices architecture.
Misconceptions on the matter:
Having web-services and rebranding them as microservices is not going to give you any benefits of Microservices Architecture(MSA).
Micro’ is a bit of a misleading term: Most developers tend to think that they should try to make the service as small as possible. This is a misinterpretation.
Guidelines for Designing Microservices:
Four major Key Design Guidelines
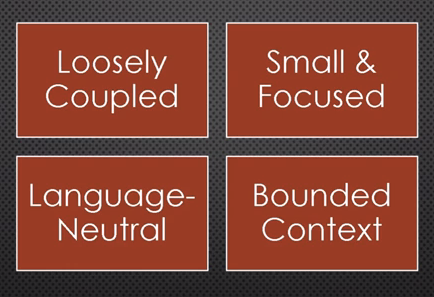
Loosely Coupled: Make sure the microservices design ensures the agile/independent development and deployment of the service.
Small & Focus: Having a limited and focused business scope for a microservice helps us to meet the agility in the development and delivery of services.
Language-Neutral: Programming language selection for microservice should be derived from the business requirement, not another way around.
Bounded Context: During the designing phase of the microservices, we should find their boundaries and align them with business capabilities.
Last updated